Wednesday, January 21, 2009
YOGA FOR HEALTH & FITNESS
Introduction:
Yoga, is a Sanskrit word meaning "union" is primarily associated with "asanas", or exercises that aim to maintain good health and concentrates on the emotional and psychological health of a patient along with his physical condition. The practice of yoga has been prevailing in India from several centuries though yoga as a career option has become popular in the recent past because of its curative powers.
History:
One saint by name Patanjali was the first to write the treatment on Yoga Sutra about 2200 years ago. Yogic practice was present even in Indus valley civilization (3300 BC), Vedas (900 BC), Upanishads (900 BC), Mahabharatha
(500 BC) also mention about Yoga.
Benefits:
Health and fitness have become areas of major concern in the fast life style of today. Yoga, probably the oldest fitness regime existing in the world can provide solution to all such health problems.
They have been found to be extremely effective in:
Increasing flexibility of the body and freeing
all the energy blocks. Besides increasing
flexibility, this leads to a healthier body.
Helping to lose excess flab and weight - another cause of ill health. Massaging the internal organs of the body and the rarely stimulated parts such as the thyroid gland.
Helping to treat several health disorders - common ones such as backaches and arthritis, asthama etc. It is recommended to include some form of yoga positions and preferably a yoga routine in your life.
Daily Yoga Routine :
Yoga routines will vary depending on the purpose for which you seek to do yoga - it may be for better fitness or for specific ailments.
1) Yoga Nidra / Yogic sleep will progress from a short introduction of 15 minutes in the first week and through more advanced aspects of awareness with each week.
2) The Asanas or yoga positions for beginners will progress from very simple Anti-arthritis series through to the Standing and Balancing postures.
3) The powerful Pranayama techniques begin with a few rounds and go up to more rounds with longer breath controls.
4) Meditation for mental relaxation.
Yogasanas :
Yoga Positions maintain the right circulation in body parts and help in channeling energy. The best part is that there is no age limit, disease or physical capability. In fact, we can use definite yoga routines for specific conditions.
Yoga has simple and effective body movements that strengthen one's back, firm the stomach, and redistribute body weight. Yoga exercises stretch and tone the body muscles. They increase endurance and improve flexibility.
Yoga Asanas or positions are the best among all exercises for toning muscles, lubricating joints and massaging the body. Asanas exercise the nerves, glands, ligaments, and muscles.
Although asanas are very powerful, the effect becomes dramatic when they are done the right way. The mind must be in harmony with the body movements. For this it is essential to train both body & the brain.
There are several simple positions as well as more complex ones. Always begin with simple poses and gradually move towards the complex ones. It is not as if maximum benefits cannot be achieved with simple positions, but it be acceptable by the body.
Yoga For Disease :
Like everyone, if you are interested in doing the right set of yoga exercises meant for just YOU!!
" " has brought out various yoga exercise plans best suited to everyone.
Yoga has postures & breathing techniques for almost all diseases, health disorders, allergies, pains etc. Many of the exercises are simple and have a magical effect on most disorders.
Yoga for Digestive Disorders :
Yoga for Digestive DisordersJust like the face turns red when one is angry, the stomach lining turns red too. And it pours out large amounts of acid and enzymes. Anger, fear, jealousy, anxiety, tension etc. are emotions which influence not only the quality and quantity of secretions in the stomach and intestine, but also alter the blood flow and the motility of the intestine. Many ailments of the digestive system starting from the mouth to the rectum are traceable to stress and a modern lifestyle.
Yoga for Back Pain :
Yoga for Back Pain With a comprehensive understanding into the dynamics of back pain, This is designed for persons with back pain as well as yoga therapists. It aims to show how the back works in health and disease as well as the yogic way of handling the problem.
Yoga for Arthritis :
A complete and wholesome insight into Arthritis is first obtained, followed by clear instructions with yoga exercises for the same. A complete yogic approach to managing arthritis is taught through a range of postures, breathing techniques, cleansing techniques as well as relaxation techniques.
Yoga for Anxiety and Depression :
We all experience anxiety or depression at some point or the other in our lives. However, depression and anxiety take the form of disease when their effects are prolonged and disturb the quality of life. This problem has become quite rampant in our affluent modern and progressive societies.
Yoga for Diabetes (Mellitus) :
Diabetes is a lifestyle related condition due to an imbalance in handling a glucose load and is NOT a disease. It is one of the several lifestyle related chronic conditions with an end result of complications that are related to early aging changes resulting in blockage of small and large arteries.
Yoga for Infertility :
Importance of Yoga :
At the outset, we must understand what is the gain out of this wonderful practice.
More importantly, yoga is extremely effective in :
Increasing Flexibility – yoga has positions that act upon the various joints of the body including those joints seemingly unrelated “non strenuous”.
Increasing lubrication of the joints, ligaments and tendons – the well researched yoga positions exercise the different tendons and ligaments of the body.
Massaging of ALL Organs of the Body – Yoga is only form of activity which massages all the internal glands and organs of the body, Yoga acts in a on the various body parts. This stimulation and massage of the organs in turn benefits us by keeping away disease.
Complete Detoxification – By stretching muscles and joints as well as massaging the various organs, yoga ensures the optimum blood supply to various parts of the body. This helps in the flushing out of toxins from every nook and cranny as well as providing nourishment. This leads to benefits such as delayed ageing, energy.
Yoga through mation works remarkably to achieve this harmony and helps the mind work in sync with the body. Moreover, stress which in reality is the #1 killer affecting all parts of our physical, endocrinal and emotional systems can be corrected through the wonderful yoga practice of mation.
In fact yoga = mation, because both work together in achieving the common goal of unity of mind, body and spirit – a state of eternal bliss.
The mative practices through yoga help in achieving an emotional balance through detachment.. The ultimate goal of the yogis was “self realization” or “enlightenment”,
Advice and Precautions
The very best time to practice yoga is in the morning before breakfast. Upon waking, empty the bowels, shower if wish, then commence the day with your regime of yoga practices. The second conductive time is early evening, around sunset.
Integral yoga is a balanced recipe which maintains: that to get the best from yoga practice, Mix and match the necessary elements of practice which will improve and enhance spiritual growth and awareness.
Yoga Positions (Asanas) may be practiced at any time of day except within 2-3 hours of having eaten. We can do postures when the body feels stiff, tense, tired or hyped-up. Be aware not to do too many over-stimulating postures just before bedtime. Asanas are best practiced first in yoga routine, followed by breathing (Pranayama) and then mation.
Pranayama may be practiced at any time of day except within 2-3 hours after meals. It may be done when tense or tired or when space does not allow room for postures. Pranayama is best practiced straight after asanas without breaking the flow of awareness. Pranayama is a necessary pre-requisite for successful mation.
Mation may be done at any time of day when you feel both awake and relaxed. For best results don’t do mation within 2-3 hours of eating, when sleepy, nor when mentally “hyped-up”.
Yoga Nidra can be done at any time of day, even directly after meals so long as you do not fall asleep in the practice. Don’t do Yoga Nidra when you feel tired or sleepy. More will be gained when you are awake and relaxed.
Place of Practice
It is best is to have yoga practice in fresh air in a quiet and clean place that suits the concentration and awareness .
Do not practice yoga in direct sunlight or after sun-bathing. Yoga can be done in outdoors but avoid cold wind and insects.
Awareness
Throughout a yoga practices, try to keep awareness on what you are doing.
Proceed slowly and carefully. Follow the instructions exactly.Never force or strain. Relax briefly between each practice. Remember the golden rule:
“If asanas are uncomfortable do not do it”.
Breathing
Always breathe through the nose both in and out, If there is any trouble in breathing through your nose, practice “Jala Neti” (Nasal Cleansing)
Restrictions & Precautions
There are no age limits either young or old for the practice of yoga. However the application of the techniques will vary according to the abilities of the practitioner.
1) Never practice any yoga techniques under the influence of alcohol or mind altering drugs.
2) Those with disabilities, severe, acute or chronic medical conditions should consult both with their medical practitioner and their yoga teacher to assess any dangers or difficulties which may arise.
3) There are no hard and fast dietary rules necessary to begin the practice of yoga.One does not have to give up smoking, become vegetarian, or be a purist to learn yoga.
Tuesday, January 20, 2009
PCOD-THE DISEASE THAT WORRIES A WOMAN
PCOD-THE DISEASE THAT WORRIES A WOMAN
A woman having delayed periods with excessive hair growth on face and body must think of Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD).It is the most common harmonal reproducive problem that affects 5-10 % women of child bearing age. It is a leading cause of infertility. The disorder is increased especially in young women due to changed life style & eating habits leading to obesity.
Anatomy of the ovary :-
The ovaries are two small organs, one on each side of a women’s uterus. A woman’s ovaries have follicles, which are tiny sacs filled with liquid that hold the eggs. Each month about 20 eggs start to grow, but usually only one becomes mature. When that egg matures, the follicle breaks open to release the egg so it can travel through the fallopian tube for fertilization.

Fig.1: A comparision of a Polycystic Ovary with narmal Overy.
Development of the PCOD :-
In women with PCOD, the ovary doesn’t make all the of the harmones it needs for any of the eggs to fully mature. They may start to grow and accumalate fluid. But no one egg becomes large enough. Instead, some may remain as cysts. Since no egg matures or is realeased , ovulation does not occur & the harmone progesterone is not made. Without progesterone, menstrual cycle becomes irregular or absent. Also,cysts produce male harmones(androgens).

Fig. 2: Laproscopic picture showing Polycystic Ovary
Signs & Symptoms:-
Ovaries are enlarged, they have smooth & whitish outer surface. the ratio of
LH (Luteinizing harmone) to FSH (Follicle stimulating harmone) is greater than 1:1, as tested onDay 3 of the menstrual cycle. There will be harmone imbalance. Testosterone & insulin levels are rised.
The lady may have excess hair on face, chest (Hirsutism). Her cycles will be irregular ,scanty & sometimes there may be no periods at all. She may become obese, diabetic& infertile. She may also have hair loss, pimples & decreased sex drive.
Diagnosis of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome :-
PCOD can be diagnosed by Physical examination, Pelvic ultrasound, Laproscopy, MRI, CT scans, Harmone levels, & measurement of Sugar levels in the blood.
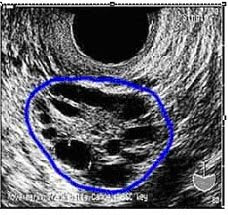 Fig 3: Vaginal scan showing PCOD
Fig 3: Vaginal scan showing PCODVaginal ultrasound scan
Vaginal ultrasound shows that the ovaries are enlarged; & there are multiple small cysts in the ovaries. These cysts are usually arranged in the form of a necklace along the periphery of the ovary.
Treatment of PCOD :-
PCOD is a common readily treatable disorder. Some of the treatment options are:-
1.Using Birth control pills : Low-dose oral contraceptive pills can regulate menstrual cycles, reduce male harmone levels.
2. Weight loss : Maintaining a healthy weight by exercise can help to cure PCOD. Metformins helps in loosing weight & also controls insulin level.
3.Fertility Medications : clomiphene(tablets) & Gonadotropins(injections) can be
used to stimulate the ovulation
.

Fig 4: Overian drilling by laproscopy
4. Medicine for increased hair growth: Spironolactone is a blood pressure medicine leads to decrease the abnormal hair growth (hirsutism).
5. Surgery: Ovarian drilling is done by Laproscopy. Cysts are punctured by electric
current This helps in ovulation & reducing male harmone.
Conclusion :-
PCOD is one of the commonest problems faced by women. Luckily it is curable. Women with PCOD must reduce the weight by strict diet & exercise. Early diagnosis and prompt proper treatment can cure the disease.
Monday, January 19, 2009
GIFT YOUR CHILD WITH BIO-INSURANCE BY STEM CELLS
Stem cells are master cells that can be transformed into various specialized cells in our body like a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a brain cell etc. These cells have the potential to regenerate, divide, repair or replace damaged cells, which helps in the treatment of over several endangering diseases like Cancer, Leukemia, etc.

TYPES OF STEM CELLS :-
There are 3 types of stem cells :
1. Embryonic stem cells : These cells are seen at the early stages of a fertilized egg called a blastocyst.
2. Adult stem cells : These are seen in the bone marrow in both children & adults.
3. Umbilical cord stem cells : These are seen in the umbilical cord of a fetus. They can be collected at the time of delivary.
All these three types of stem cells can be collected from their respective sites & can be used for growing other types of cells.
PROPERTIES OF STEM CELLS :-
The stem cells have an unique potency to differentiate into specialized cell types. Their potency can be classified into three types
a) Totipotent : Ability to give rise to any type of cell.
b) Multipotent : Ability to give rise to some specific types of cells.
c) Unipotent : Ability to give rise to its own type of stem cells.
Let us know more about the Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells which are considered as Gift of Life ! They can be used as a Bio-insurance for the future health of a child.
CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS :-
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord after it has been cut, but while it is still attached to the placenta. This blood is rich in stem cells, which are able to grow in any type of body cell. Cord blood is collected, processed and cryogenically preserved for future medical use.

Fig 2: Use of cord blood to grow different types of cells
COLLECTION OF CORD STEM CELLS :-
Cord blood is collected immediately after birth by a doctor or nurse. This blood can be frozen & stored privately for family use or donated to public cord blood banks.
We have only one chance at birth, to collect the Cord blood stem cells.

USES OF CORD STEM CELLS :-
Both the Versatility & availability of umbilical cord blood stem cells can be used to treat leukemia and other cancers and also blood & immune diseases. There are more than several different disorders which can be treated with cord blood. It can be used in place of a bone marrow transplant.
STEM CELL BANKING :-
Stem cells can be stored in a stem cell bank by “Cryopreservation” for future use of a person. Sometimes even siblings or some other person can also use these stem cells. Intensive research is going on in the field of Stem Cell Preserving, Utilizing them for future use in the treatment of diseases and for therapeutic cloning.
STORAGE OF CORD STEM CELLS :-
By preserving the baby's stem cells, we have a guaranteed source of perfectly matched cells in the event a life threatening illness develops and the cells are used in the emergency situations like accidents.

Fig 4: Stem cell differentiating into kidney cells
TREATABLE DISORDERS OF STEM CELLS :-
There are more than 75 diseases has been listed as treatable diseases. Some of them are Cancers, Thalasemia, Blood disorders, Immune deficiencies, Musculoskeletal disorders, Connective tissue disorders, Metabolic disorders, Storage disorders, Alzeimer’s disease, Cartilage regeneration, Diabetes, Heart disease, Liver disease, Multilpe sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy, Spinal cord injury, Stroke etc.,
CONCLUSION:-
We can only have one chance at birth to collect stem cells from the cord blood. These stem cells can be used in future for curing many illness that may occur in future for the baby when it grows or even for other family members. It is something like a bio-insurance for life of a child.
Friday, January 16, 2009
IN VITRO FERTILISATION (IVF)
IN VITRO FERTILISATION (IVF)
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a technique in which egg cells are fertilized by sperm outside the woman’s womb. IVF is a major treatment in infertility when other methods of achieving conception have failed. The process involves hormonally controlling the ovulatory process, removing ova (eggs) from the woman’s ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a fluid medium. The fertilized egg (zygote) is then transferred to the patient’s uterus with the intent to establish a successful pregnancy.
IVF Method
Ø Ovarian stimulation
Ø Oocyte retrieval
Ø IVF laboratory
Ø Embryo transfer
Ø Post-transfer
Success rates
There are many reasons why pregnancy may not occur following IVF and embryo transfer, including
· The timing of ovulation may be misjudged, or ovulation may not be able to be predicted or may not occur
· Attempts to obtain eggs that develop during the monitored cycle may be unsuccessful
· The eggs obtained may be abnormal or may have been damaged during the retrieval process
· A semen specimen may not be able to be provided
· Fertilization of eggs to form embryos may not occur
· Cleavage or cell division of the fertilized eggs may not take place
· The embryo may not develop normally
· Implantation may not occur
· Equipment failure, infection and/or human error or other unforeseen and uncontrollable factor, which may result in the loss of or damage to the eggs, the semen sample and/or the embryos.
Potential complications
The major complication of IVF is the risk of multiple births. This is directly related to the practice of transferring multiple embryo at embryo transfer. Multiple births are related to increased risk of pregnancy loss, obstetrical complications, prematurity and neonatal morbidity with the potential for long term damage. Strict limits on the number of embryos that may be transferred have been enacted in some countries (e.g., England) to reduce the risk of high-order multiples (triplets or more), but are not universally followed or accepted. Spontaneous splitting of embryos in the womb after transfer does occur, but is rare (<1%) and would lead to indentical twins. Recent evidence suggest that singleton offspring after IVF is at higher risk for lower birth weight for unknown reasons.
Another risk of ovarian stimulation is the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Allergy is a disorder of the immune system often referred as atopy. Allergic reactions occur to enironmental substances known as allergens. These reactions are acquired, predictable and rapid. Allergy is one of four forms of hypersensitivity. In some people, severe allergies to environmental or dietary allergens or to medication may result in life-threatening reactions and potentially death.
Causes:
Risk factors for allergy can be placed in two general categories, namely host and environmental factors. Host factors include heredity, sex, race, and age, with heredity being by far the most significant. The four main environmental factors are alterations in exposure to infectious diseases during early childhood, environmental pollution, allergen levels and dietary changes.
Signs and Symptoms:
Many allergens, such as dust or pollen, are airborne particles. In these cases, symptoms arise in areas in contact with air, such as eyes, nose and lungs. The common symptoms of allergy and its affected organs are:
Nose- Swelling of the nasal mucosa
Sinuses- allergic sinusitis
Eyes- redness and itching
Airways- sneezing, coughing, bronchoconstriction, wheezing, swelling, sometimes out right attacks of asthma
Ears- feeling of fullness, pain and impaired hearing
Skin- rashes, such as eczema and hives
Gastrointestinal tract- abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting, diarrhea
Diagnosis:
Before a diagnosis of allergic disease can be confirmed, the other possible causes of the presenting symptoms should be carefully considered. There are two types of diagnosis namely:
Skin testing-
Blood testing-
SEMEN BANK
INTRODUCTION: In our society it is common that people borrow or lend help from others when they require something. This even includes several human body parts like tissues, heart, liver, kidney, lungs, skin, cornea, eye, bone etc.
In recent medical revolution even sperms, eggs & embryos from one person are obtained for the use of others. Certain medical banks have been established for recovering, processing, preserving & providing these body parts for the required persons. The one that stores the semen is called semen bank.
SEMEN BANK: A semen bank is also called as Sperm bank or Cryo bank. It is a facility that collects, processes, preserves and stores human sperm from known or unknown donors, for the purpose of artificial insemination. The process of preservation is also called as cryopreservation.
HISTORY OF CRYOPRESERVATION: In 1940’s veterinary doctors started freezing & storing bull semen & artificially inseminated the cows. In 1950’s same technique was utilized for storing human semen for artificially inseminating women resulting in first childbirth.
NEED FOR SEMEN BANK: Mainly there are two main reasons for storing semen, they are:
1. OWN USE STORAGE: There are several situations where a person may feel to store his own semen for future use. Some of the conditions are: -
a. Men who are suffering from serious diseases like cancer, which requires treatments like radiation therapy, chemotherapy or surgery that will cause infertility.
b.Men who want to undergo vasectomy.
c.Men who are engaged in high risk occupations, including at-work exposure to radiation or dangerous chemicals.
2. DONOR SEMEN STORAGE: Some men may opt to donate their sperms for the use of others. It is important to know that the donor is giving his genes to another known or unknown couples. It may be voluntary donation or for monetary benefits.
ELIGIBILITY OF THE DONOR: All healthy men between the age group of 18- 45 can donate the semen. There are some conditions to be followed before donating.
Donor should have good physical & mental health. He should be free from all infectious disease, sexually transmitted diseases like HIV, hereditary diseases, hepatitis etc.
TECHNIQUES OF SEMEN COLLECTION:
Donor should not have sexual intercourse for at least three days prior to donation.
Specimen must be obtained by masturbation.
The entire specimen should be properly collected directly into the sterile container provided by the laboratory.
If the semen is collected outside the semen bank then it should be handed over to the semen bank within 1 hour of collection & it should be kept warm by carrying in the pocket.
 Fig 1: A lab technician is seen taking out frozen semen from liquid nitrogen tank.
Fig 1: A lab technician is seen taking out frozen semen from liquid nitrogen tank.TECHNIQUE OF CRYOPRESERVATION: The collected semen is first analyzed for its quality. Then the semen is washed with certain reagents & then mixed with the preservative. It is then stored in vials that are properly labeled. This vial is then kept inside a liquid nitrogen tank. The temperature inside these tanks is maintained at –196C.
DURATION OF STORAGE: Semen can be stored by cryopreservation for indefinite time. It can be stored even for 30 years. However it is used as early as possible. It can also be transported to long distances through liquid nitrogen flasks.
DISADVANTAGES: A major risk of insemination of frozen sperm is the failure of fertilization and pregnancy. The viability and motility of frozen-thawed sperm is usually lower than that of fresh sperm.
CONCLUSION: Semen banks are a boon & ray of hope for infertile couple. It has been socially, legally, ethically & morally accepted by one & all. Just like blood donation, semen donation also serves for a noble cause. It has enabled many couple to conceive, who would otherwise have not been able to have children on their own. Healthy men should voluntarily come forward for the semen donation & remember
“Donate semen & give life”.
Thursday, January 15, 2009
When the sex of a person is doubtful - INTERSEX
Every person in the society is labelled as male or female by the family and the law. However, there are few unfortunate people who does not fit into into this definition of male or female. There are some men with female characters, behaviour and organs and vice versa. Also, there are some men who mentally feel that they are female and vice versa. There are also few people in whom sex determination is extremely difficult. All these people are called as Transexuals or Intersexuals or Hermaphrodites. This occurs in about one in 5000 of the people.
WHAT IS GENDER AND SEX OF A PERSON?
Gender and sex are quite separate things. But many a times they are used to give the same meaning. Sex is the physical form and function of a person. Gender is the assigned status of a person being identified as male or female.
HOW SEX IS DETERMINED?
The criteria for correct sexual determination of a child include-
1. Chromosomal Sex
2. Gonadal Sex ( ovary-female;
testis-male)
3. Hormonal Function
4. Internal and External sex organs
5. Assigned sex (at birth)

 MALE
MALECAUSES FOR TRANS-SEXUALITY: The causes for trans-sexuality may be due to two factors namely genetic causes and hormonal causes.
 TRANSE -SEXUAL SYMBOL
TRANSE -SEXUAL SYMBOLThe genetic causes can be seen with development of foetus. A foetus bearing an XY chromosome pair develops into a male and a foetus with an XX chromosome pair develops into a female. Other sex chromosome combinations are possible such as X0 (Turner’s syndrome), XXX, XXY (Klinefelter’s syndrome), XXXY, XYY and so on.
The hormonal causes is due to hormonal imbalance. The increase in the production of male hormone androgen makes a female with male characteristics. The increase in the production of femal hormone esterogen make a male with female characteristics.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: The signs and symptoms of trans-sexual male or female are as follows:
1. Person predominantly male with female characters: This person will have XY chromosome pair, with feminine characters such as enlarged breasts, absence of male characteristic hair, underdeveloped penis and testes.
2. Person predominantly female with male characteristics: This person will have XX chromosome pair, with underdeveloped breasts, distribution of hairs like male (hirsutism), and vagina which are infertile. Uterus and ovaries may be absent or underdeveloped.
PROBLEMS FACED BY TRANS-SEXUALS: In the ancient world, trans-sexuals were considered magical, kin to the gods or spirits and as a medicine man working with magic. In our country, they are treated in a hypocritical fashion and they are often paid to attend and bless weddings and to act as spiritual and social advisors. Most of times, the person will be impotent or infertile.
But nevertheless, at every moment they are ignored and suppressed by the society. They face the violent unacceptance of the society, medical establishment, common loss of all family and friends and cost of treatment. They are even devoid of getting a decent care from the society. The agony they experience can lead to self destruction.
TREATMENT: The kind of treatment provided will depend on the individual needs of the patient and subject to negotiation between the consultants involved, patient’s family doctor and the patient. The available treatment are hormone therapy, surgical reconstruction and counseling.
THE LEGAL POSITION: The present legal position is that trans-sexuals lose a substantial part of their civil liberties. They are placed outside the remit of the Sex Discrimination Act. They do not have their birth certificates to show their gender status. They cannot marry a member of the other gender. They do not have right to vote.
CONCLUSION: Trans-sexuals suffer because they are trapped in a body of the wrong sex. Of course “truth is always bitter”, but a person should not be punished for no fault of his. Society should accept them as descent members. They must be given all the rights of a person. They must be treated with dignity.
CAESAREAN SECTION
CAESAREAN SECTION
A caesarean section or c-section, is a form of assisted childbirth in which a surgical incision is made through a mother’s abdomen and uterus to deliver one or more babies. It is usually performed when a normal delivery would put the baby’s or mother’s life or health at risk. In recent times it is being performed upon request or sometimes indiscriminately for births that would otherwise have been normal.
The word caesarean comes from Roman word “Lex Caesarea” meaning to cut open the mother abdomen to deliver the baby.
Indications: Doctors have different opinions about the necessity of caesarean. Some of the indications are: having high blood pressure, having had a previous caesarean, having twins or triplets, slow progress during labour, and having a very large baby or an abnormal positioning of the baby. The indication viewed in the mother’s condition are- unable to push the baby out and placenta placed lower down in the uterus.
Contraindications: C-section is contraindicated when the mother’s medical condition does not permit her to undergo any surgery. A caesarean delivery may not be recommended if the fetus has abnormality or known anomaly that may lead to death.

Anaesthesia: The operation is done under either a general anaesthetic or, a spinal anaesthetic.
Risk factors: A C-section birth involves major abdominal surgery, so the benefits need to be weighed against the risks in each case.
Risks for the mother:
Women may land up in problems such as: infections, haemorrhage, blood clots, damage to the bowel or bladder, fallopian tubes with possible effects on fertility.
A C-section will usually: require a hospital stay, standing and walking around, getting out of bed is difficult and painful.
Risks for the baby:
The major risk for the baby is breathing difficulties.
Cost factor: Normal deliveries is four times safer to the mother as well as for the child than in C-section.
Complications: As with any major operation there is a risk for complications related to your heart or your lungs, or an injury to spinal cord. Aches and twinges may be felt in the wound. It may result in numb patches in the skin around the wound.
he complications of babies delivered through caesarean section include scratches or cuts, fractures of the skull or long bones and serious brain or nerve damage.
Disadvantage of C-section: One woman in 2,500 who has a caesarean section may die, compared to a rate of one in 10,000 for a vaginal delivery.
Alternative for C-section: The decision to deliver your baby/babies by C-section has been made by your obstetrician and yourself. If you are unhappy with this decision, then you should speak to your family doctor or take a second opinion from another obstetrician.
Avoiding C-section: There are ways which may help to reduce the likelihood of a C-section:
If your baby is breech, having the baby turned.
In the later part of pregnancy, using upright, forward positions to help the baby get into a good position for labour.
During labour, keeping upright and mobile so that labour progresses well.
Precautions:
C-section is a major surgery. Hence adequate rest and post operative care must be taken by the woman.
Start walking soon as it will prevent blood clots from forming.
Avoid subsequent pregnancies or give adequate spacing before becoming pregnant again.
Conclusion: There is an increasing tendency to go for C-section delivery in the private hospitals and nursing homes. In some private maternity homes C-section delivery is as high as 75%.This is done in order to escape from pain which is a bad precedence. Subjecting a lady for C- section for monitory gain is unethical. It should be strongly condemned. Alternative methods of delivery must be viewed or considered before taking up for C-section. Mother should wait or bear the pain in order to undergo the normal delivery.
The large difference in the rates of C-sections in women in the Govt and private hospitals is due to more unwanted caesarean sections among private hospitals rather than a real medical indication for surgery.

Cervical cancer is malignant cancer of the cervix uteri or cervical area, the lower part of the uterus that enters the vagina. Normal cervical cells may gradually undergo changes to become precancerous and then cancerous. It may be present with vaginal bleeding but symptoms may be absent until the cancer is in its advanced stages.
Cervix :
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb). The upper part, or body, of the uterus, is where a fetus grows. The cervix connects the body of the uterus to the vagina.

Cervical Cancer :
Cervical cancer (fig 2) develops in the lining of the cervix. This condition usually develops over time. Normal cervical cells may gradually undergo changes to become precancerous and then cancerous.
FIG 2 : Showing cervical cancer
Cervical cancers and Cervical pre-cancers are classified by how they look under a microscope. There are two main types of cervical cancers:
Squamous cell carcinoma: These cancers are from the squamous cells that
cover the surface of the exocervix (part next to vagina).
Adenocarcinomas: These develops from the mucus-producing gland cells of
the endocervix (part close to the body of uterus).
Less commonly, cervical cancers have features of both squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. These are called adenosquamous carcinomas or mixed carcinomas. About 80% to 90% of cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. The remaining 10% to 20% of cervical cancers are adenocarcinomas.
Causes :
Cervical cancer is more common in women middle aged women and in women of poor socioeconomic status
The cause of scervical cancer is unknown. But usually two types of infections namely Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) & Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) are known to cause cervical cancer.
Risk Factors :
Following women have more risk of getting cervical cancer than their counterparts.
· Women with multiple sexual partners.
· Women suffering from sexually transmitted disease (STD)
· Smokers.
Signs and Symptoms : Symptoms that may occur includes:
· Abnormal vaginal bleeding (e.g., spotting after sexual intercourse, bleeding between menstrual periods, increased menstrual bleeding) .
· Abnormal (yellow, odorous) vaginal discharge.
Painful sexual intercourse
Low back pain
Cervical cancer that has spread to other organs may cause constipation. It may also cause blood in the urine, abnormal opening in the cervix(fistula) & urinary obustruction.
Diagnosis :
The diagnosis are based on the results of the physical exam and biopsy. Many of the diagnostic tests described below are not necessary for every patient. Some of the diagnostics tests for cervical cancer are:
· Medical history and physical exam done to examine the cervix and cervical cells.
· Cystoscopy, protoscopy and examination under anesthesia- examination of bladder and rectum.
· Imaging studies- Chest x-ray, ultrasound scanning, Computed tomography (CT),
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Intravenous urography and Positron
emission tomography.
Prevention :
Following measures may deduce the chances of getting cervical cancer in a women.
Not smoking
· Having regular Pap smears
· Using condoms
· Limiting the number of sexual partners
Treatment :
Treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage of the disease. Some of them are:
Surgical treatment involves removal of entire uterus and adjoining affected organs
Radiation: After surgery, radiation may be used to decrease the risk for recurrence.
Chemotherapy uses toxic drugs, tablets or injections to destroy cancer cells.
Conclusion :
Cancer of the cervix often can be cured, if it is detected and treated early.It is very important to every women especially after the age of 30 years to undergo annual medical check up which should include a pap smear.
Wednesday, January 14, 2009
WOMENS AND NUTRITION
Even after 61 years of Independence, more than 55% of women are suffering from malnutrition. To over come this the Government of India has declared the first week of September as “National Nutrition Week”. This is the 27th year of celebration of the National Nutrition Week. This is the special occasion to focus on the various forms of malnutrition among girls and women. It is all our responsibility to ensure proper nutrition to girls and women thus, build a strong Nation.
Women and girls are the worst sufferers of the various forms of malnutrition because of their increased nutritional needs and low social power. Nutrition of women is not only important for their own health but it determines the nutrition and health of the future generations also.
Reason for malnutrition among females:
Gender discrimination within home is often manifested in unequal access to food and inferior quality of food provided to girl children.
Early marriage, early pregnancy aggravates both under-nutrition and anaemia and result in adverse outcome of pregnancy including low birth weight baby.
Frequent menstruation, pregnancy, delivery, lactation, abortion and still births, and menorrhagea can create malnutrition.
Poverty and lack of education
Economics of nutrition in women: A healthy girl child and woman is an asset to the Nation. If women become healthy and strong they can give birth to the healthy baby who are asset to the Nation. Recent evidence suggests that under nutrition levels in India are among the highest in the world.
Nutrition for Girls and Women: Women and girl requires more care and they require balance diet because they undergone several steps in their life cycle such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, delivery, lactation, abortion & still births, and menopause. Pregnancy is the most critical period as requires extra calories for both mother and a baby. Even before pregnancy begins, nutrition is a primary factor in the health of mother and baby. A well-balanced diet before conception contributes to a healthy pregnancy.
A Balanced Diet: A well balanced diet that is high in fibre, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals and low in saturated fats will help a woman to stay fit to face the challenges of a reproductive life. A balanced diet consists of food from the five basic food groups in the correct proportions. That is:
Cereal group -Rice, Jowar, Ragi, Wheat, Bajra, Maize, Roots. Tubers have important nutrients and vitamin B. Ragi is rich in iron. Rice and wheat should not be polished. Rice and wheat husk contains vitamin B. Brown bread is better than white bread which contain Thiamine, Niacin, Iron.
Fats and oils group - Margarine, oils, salad dressing have important nutrients - essential fatty acids, vitamin A, D and E.
Meat - Meat, chicken, fish, eggs contains important nutrient -proteins, Iron, vitamin B12 is recommended.
Alternatives for meat for vegetarians - For vegetarian’s legumes, including leafy vegetables which are rich in iron, dhal, Soya should be taken.
Milk and milk products - Milk, cheese, curds have important nutrients - Calcium, phosphorus, vitamins.
FIG SHOW A BALANCED DIET
Fruit and vegetables - all types have important nutrients include vitamin &
minerals especially vitamin A, vitamin C and fibre.
Having food from the five basic food groups during the day ensures that the diet consists of varieties of nutrients.
Tips for healthy eating
Eat plenty of vegetables, Fruits and vegetables contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals needed for a healthy child.
Herbs Culinary herbs are herbaceous (leafy) plants that add flavour and colour to all types of meals. They have also been used for centuries to preserve food due to the presence of antioxidants.
Healthy cooking tips. In many cases, favorite recipes can be modified so they offer a lower fat content. Non-stick cookware can be used to reduce the need for cooking oil. To keep valuable nutrients, microwave or steam your vegetables instead of boiling them.
Fibre regulates bowel activity, keeps mouth and jaws healthy and lowers blood cholesterol
Cancer and food. Some cancers are influenced by our daily diet. Cancers of the stomach, bowel, lung, prostate and uterus are more likely to develop if diet is high fat and low fibre.
Calcium for your bones: Milk and foods produced from milk — cheese, curds, ice-cream and some custard — are the richest source of calcium.
Vegetarians need to monitor their food intake to make sure that they get enough iron, zinc, B vitamins, protein, vitamin D and calcium.
Conclusion
Good nutrition is important for everyone especially for Women and girls. They require extra nutritional nourishment due to their physical and physiological nature. Nutrition is the cornerstone of National Development. Healthy women can make nation strong and healthier. It is the right of every girl child and women to get good nutrition food.
MOLAR PREGNANCY
A molar pregnancy is one of the serious complications of pregnancy. It happens when something goes wrong during the fertilization process at conception. In a molar pregnancy, the early placenta develops into a fast-growing mass of cysts (hydatidiform mole) in the uterus. It occurs in about 0.5to 1% of the pregnant woman.
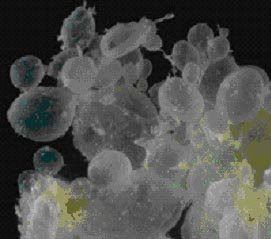
Figure 1: Molar pregnancy looking like cluster of grapes.
Complete molar pregnancy: In this pregnancy, the fertilized egg has no maternal chromosomes and the chromosomes from the father’s sperm are duplicated, so there will be two copies of chromosomes from the father and none from the mother. Complete molar pregnancies have only placental parts, and form when the sperm fertilizes an empty egg. Because the egg is empty, no baby is formed. The placenta grows and produces the pregnancy hormone, called HCG, so the patient thinks she is pregnant. Instead, the placenta forms a mass of cysts that looks like a cluster of grapes.

Figure 3: Complete molar pregnancy with 46 chromosomes, two copies of chromosomes from the father and none from the mother.
Partial molar pregnancies: In most partial molar pregnancies, the fertilized egg has the normal complement of chromosomes from the mother but double the chromosomes from the father, so there are 69 chromosomes instead of the normal 46. In this case, there’s some placental tissue among the cluster-like mass of abnormal tissue. The embryo does begin to develop, so there may be a fetus, or some fetal tissue, or an amniotic sac. The baby has too many chromosomes and almost always dies in the uterus.
 Figure 4: partial molar pregnancy with 69 chromosomes, normal complement of chromosomes from the mother but double the chromosomes from the ಫಾಥೆರ್
Figure 4: partial molar pregnancy with 69 chromosomes, normal complement of chromosomes from the mother but double the chromosomes from the ಫಾಥೆರ್
Risk factors: Unfortunately, any woman, no matter what her age, race or medical background, can develop a molar pregnancy. However, it is more common in women over the age of 40. It is common in women having a previous molar pregnancy or miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. It is also common in women suffering in vitamin A deficiency.
Signs and Symptoms: Symptoms include: A molar pregnancy typically triggers common signs of pregnancy—a missed menstrual period, breast tenderness, fatigue, weight loss, increased heart rate, heat tolerance, sweating, irritability, anxiety, muscle weakness, increased urination, and morning sickness. Signs of pregnancy that may develop any of the following during first trimester:
Vaginal discharge of tissue that is shaped like grapes.
Severe nausea and vomiting
High blood pressure,
A uterus that is abnormally large for the length of the pregnancy.
Levels of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be much higher than normal.
Diagnosis: Ultrasound scanning will detect molar pregnancy very easily. In the scanning the pregnancy looks like “cluster of graphes”. No fetus will be detected.
Complications: If the molar pregnancy not removed completely it may continue to grow inside. It may cause vaginal bleeding. Sometimes, it may become cancer also.
Treatment: A molar pregnancy is removed with vacuum aspiration D & C (dilation and curettage) under general anesthesia. There are high risk of developing cancer after a molar pregnancy and can be treated with methotrexate or Dactinomycin.
Precautions: Pregnancy following too soon after molar pregnancy may also increase the risk of recurrence or re-activation of the mole. Avoid pregnancy for at least six months with normal urine hCG levels or until your consultant gives you the go ahead.
Conclusion: Experiencing a molar pregnancy is extremely stressful for the woman, her partner and family. Not many people understand the physiology of such a pregnancy. It is generally best to tell loved ones that a miscarriage has occurred and that special follow up lab work is necessary. When the pregnancy itself has been “ambiguous” and the life of the mother has been at risk, it may be harder to understand and disclose all of the details.
